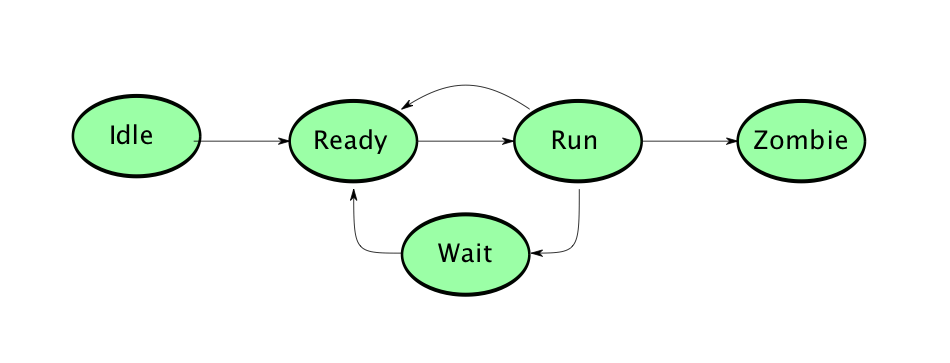
Process State Transitions
Understanding how processes transition between states is crucial for comprehending Unix process management. These transitions are triggered by various events and system calls, forming a state diagram that represents the process lifecycle.
When a process is created, it starts in the New state and quickly transitions to either Running or Sleeping, depending on system resources and scheduling decisions. A Running process can transition to Sleeping when it requests I/O operations or waits for events. It can also be moved to the Stopped state by receiving appropriate signals or transition directly to the Zombie state upon termination.
Sleeping processes transition back to Running when their waiting condition is satisfied, such as when I/O operations complete or requested resources become available. The scheduler manages these transitions, ensuring efficient resource utilization and system responsiveness.
The transition from any active state to the Zombie state occurs when a process calls exit() or is terminated by a signal. The final transition from Zombie to complete removal happens when the parent process collects the exit status, completing the process lifecycle.